Product design (a.k.a. Product sense ) is the most common problem asked during PM interviews ( e.g. Google or Facebook / Meta Product Manager ). It should not be confused with the UI-UX or system design challenges. Here, product design is a journey where you explore diverse questions and challenges pertaining to product discovery & development. The journey begins with the search for answers to Why, Who, What, Where, When and How. However, all of these need to be investigated in a limited time frame of 30-45 mins during an interview. Here is a comprehensive guide to approach such questions with various examples, points and tips to consider. Product design problems can be either case studies or open ended questions on technology /physical products.
SAMPLE PRODUCT DESIGN PROBLEMS :-
Design an app for the Louvre Museum
Design Youtube for Concert Lovers
Design a Travel app for Airport Layover
Design an alarm clock for blind
Design a solution for gardening
Design an education product for Facebook
How would you improve Instagram ?
How would you a design a pen for Scuba Divers ?
How would you monetize Whatsapp ?
If you are FB PM, how will you design a product for people moving to a new city?
As a startup, how would you build a product to combat climate change ?
The varying degree of vagueness in these problems is intentional. Some questions may have a specified goal (monetize Whatsapp), while others may have some specified users (Scuba Divers), product (Travel app), use case (Gardening) or a company (Facebook / Meta). The intent is to assess how a PM candidate organizes the provided information and discovers the absent information while navigating the path of decision making. The thought process must reflect Goal clarity, Customer Empathy, Knack for details, Creativity and Pragmatism.
10 Steps to Crack Product Design Interview
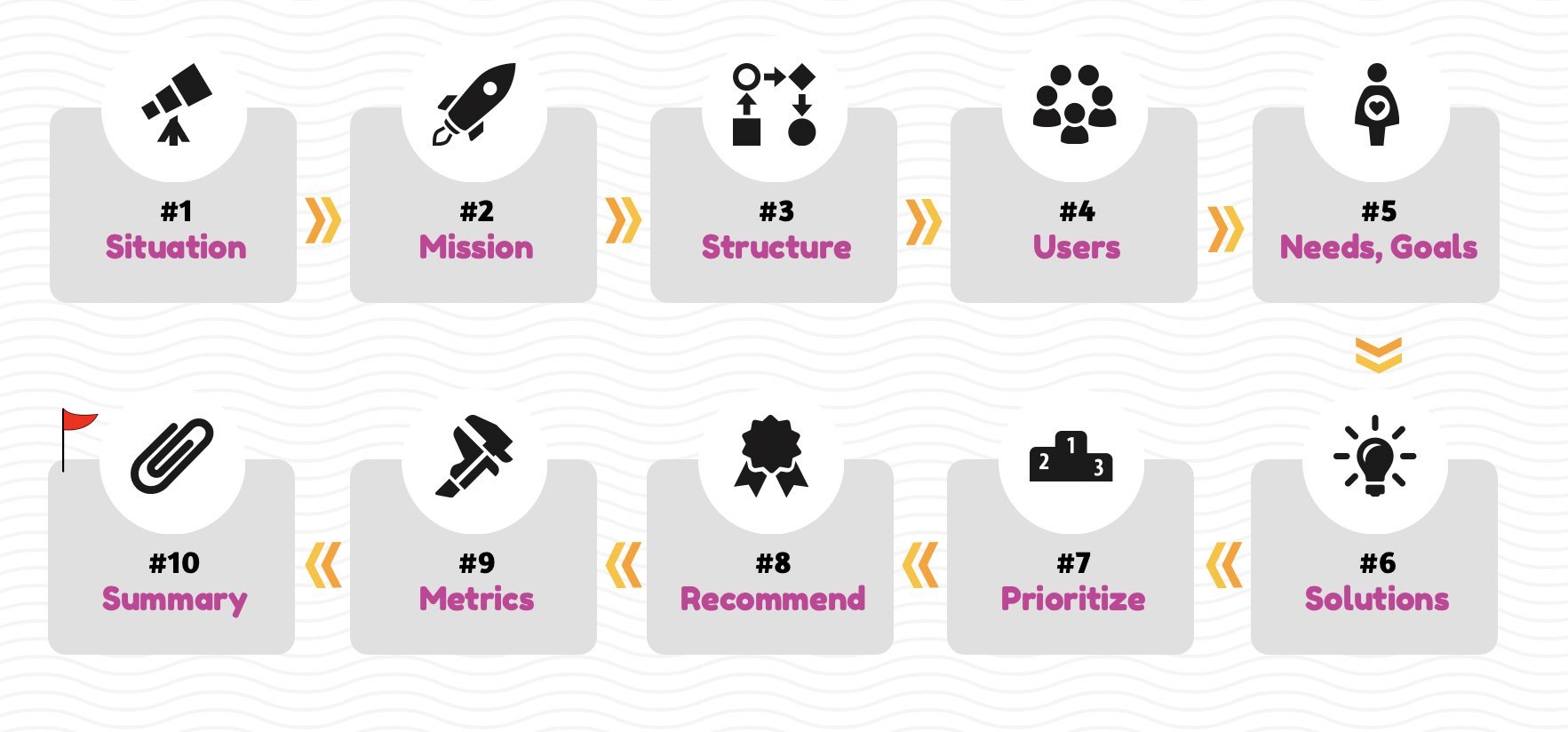
1) Situation Understanding - Ask Clarifying Questions
First, narrow down the broad problem by gathering as much information as possible. PMs are expected to thoroughly understand the problem and the underlying context to define the scope and target before moving to solutions.
Reiterate the problem to avoid any misses.
E.g. “Let me make sure that I understood the problem clearly….[state the problem statement here]”.
Also, if it is an existing product, verify your understanding of the product with the interviewer.
E.g.
“My understanding is that X product does…….” Else, clarify “What do you mean by ……. ? What is the product about ?”.
Try to understand what is the goal of this activity - “Why are we doing this ? What is the company goal ?”
CLARIFYING QUESTIONS TO ASK :-
What type of company are we? Startup, Large company
Are there any constraints/limits in terms of resources like cost, time or effort?
Considering the type of company, any goal for us? gain market share/customers?
How are people solving this problem today ?
What are the alternatives available in the market ?
Would it be safe to assume that it would be part of main App than a separate one?
Would this be a web product or a stand-alone app?
Is it an Existing or New? 0 to 1 product? Related products?
Where is the product in its lifecycle - new/growth/maturity?
Is it going to be digital or physical product?
Do we have any particular customer segment or situation like Covid I should focus on?
What market/geography the product serves?
Should we focus on any platform like android, web, desktop in particular?
Do we have any data/reason for us to focus on a particular user? flow or pain point?
Interviewers generally allow you to make assumptions but it is best to ask and clarify. Assume wherever you can but just call it out.
ASSUMPTION :-
"Scope is limited to Facebook.com both App and Web. We are not focusing on
Instagram, Whatsapp or other Facebook owned properties"
Pro Tip :-
#Try underlining key words to better understand the problem.
For e.g. - Problem: How would you improve Instagram?
Questions: What needs to be improved? UX? Monetization? Customer engagement? Are we talking about Instagram for regular users or influencers or advertisers? Mobile App or Advertisor tools?
2) Mission
Determine how the product relates to the company’s or entrepreneur’s (or rather the interviewer’s) vision. Reiterate the mission and the synergies.
MISSION :-
Facebook - Make world more connected and help people build communities.
Instagram - Allowing people to capture and share moments of their life.
To bring you closer to the people and things you love.
Google - Organize the world's information & make it universally accessible & useful.
For instance, if the given problem is around building a Travel product, it does make sense for each of the above companies as per their mission statements, . In a way, travel as a use-case is an extension of their core missions.
3) Approach - Structure
Lay down the steps of your problem solving approach. This will keep your thoughts organized and help the interviewer follow the conversation easily.
FLOW :-
Users-> Needs-> Solutions-> Prioritisation-> Recommendation-> Tradeoff-> Metrics
4) Users
PMs represent the Voice of the Customer in Business. Designing a product is not possible without thinking about its users/customers. Generally, PMs engage in a dialogue with users to better understand them and their needs. This involves research, customer interviews, FGDs and documentation of insights. However, you would proceed with user-thinking and assumptions while interviewing for PM role. Things to note -
- Consider all potential and current users
- Identify primary user and secondary user
E.g.- A product for kids will have kids as primary users, parents as customers/secondary users whereas teachers or coaches may be the other users.
User Segments
Group the product users into two or more segments (preferably three or four) based on some common traits, needs, and behaviours. It is recommended to use 3-4 characteristics to define each segment for clear segregation and representation.
Example user segments could be -
- Young professionals (M/F) of age 20-25 years with above average income
- Millennials who are Information & content seekers, Socially conscious and Tech Savvy
For more details, read segmentation
USER SEGMENTS :-
Working professional, Student, Homemaker, Parents
Demographic - Age, sex, family status, Income, Profession
Millennials(25-40), GenZs (<24 yrs), Baby boomers (40+) (timing)
High frequency, Medium frequency, Low frequency users based on usage
Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards
OTHER USERS :-
Artists, Content creators, Advertisers, Young Adults,
Parents, Kids, Elders, Students, College goers, Religious,
Working professional, Traveler, Affluent, Price Conscious,
Risk Averse, Influencer, Follower, Volunteers, Activists,
Conservatives, Digital Nomad, Hiker-Traveler, Educators
If you have identified multiple customer segments, it is ideal to prioritise and focus on just 1 or 2 segments. Clarify your logic of prioritisation (e.g. market share)
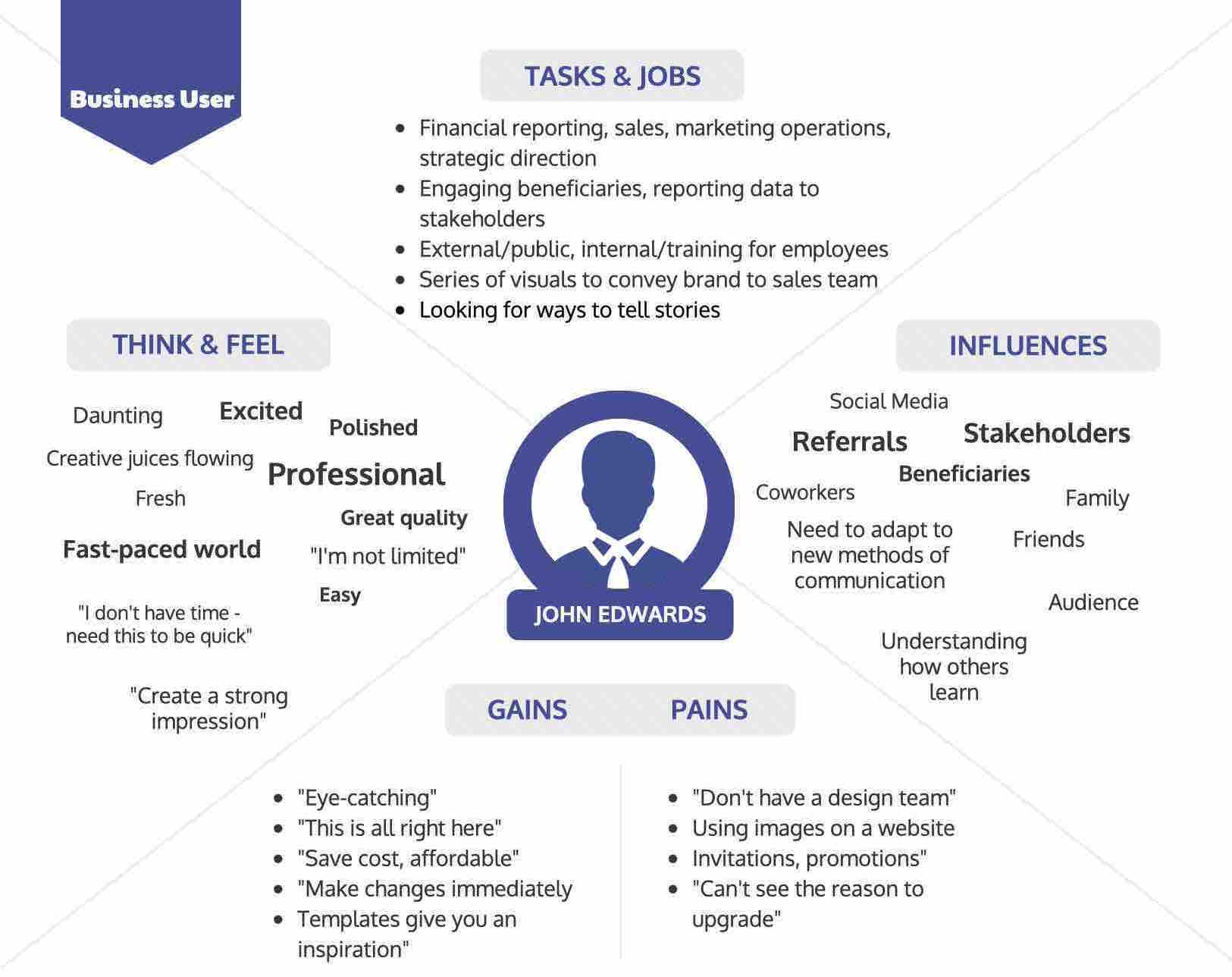
User Persona (Optional)
While building the product for a selected user group, design a detailed user persona if you have time.
This will help to uncover the user’s lifestyle, behaviours, objectives - what/ why/ where/ how/ when?
Use Cases
Once you have derived user segments, the next step is to envision the use-cases in which the product will be used. A use case is a description of how a person uses the product to accomplish a goal. E.g. in payments product, the typical use-cases are Person-to-Person (P2P), Person-to-Business (P2B), Business-to-Person (B2P) and Business-to-Business (B2B) or 4-12 yrs Kids in elementary school, home or books/dance club
USER SCENARIOS :- When, Where, Why, What, With Who ?
At this juncture, it is recommended to prioritize or eliminate user segments/use-cases after giving a reasonable justification. It often makes sense to also define the product goal immediately if you have the goal clarity.
Pro Tips :-
#Think of both supply and demand side when identifying users. For example - buyers, sellers
#PMs especially interviewers love matrix/grids. Try creating a matrix or table of User segments on one side and use-cases on the other or a grid of User demographics and their usage frequency
#After identifying the users and use-cases, ask some clarifying questions to see if the interviewer wants you to focus on anything specific.
5) User Needs, Pain points & Goals
After figuring out the right user segments and use cases, pivot to user needs, desires, motivations & objectives. User need gaps are often referred as “pain points” (e.g. limited free time for working professionals, safety for kids and mobility for people with wheelchair) Let’s say the problem is “To improve Instagram Stories” and the target user is “Gen Z, College goer, High Freq User”. The pain points here will be -
- Share updates with friends asap
- Stay updated about friends
- Engage/express socially through likes and comments
- Maintain privacy amongst network
KEY PAINPOINTS :-
Awareness, Discovery, Value, Selection, Creation, Ease, Clarity, Effectiveness,
Privacy, Authenticity, Integrity, Fairness, Relevance, Poor Experience, Support,
Community-social needs, Performance, Accessibility, Reach, Efficient, Safety
User Journey
To uncover more pain-points, put yourself in user/customer’s shoes. Envision the user journey
USER JOURNEY :-
Discover-> Reach-> Access-> Test-> Use-> Complete-> Validate-> Express-> Share -> Refer
E.g. User journey of a traveller: Decide the place -> Itinerary/route -> Activities/experiences -> Split expenses -> Share memories-photos/videos -> Review & Refer
Pro Tip :-
#Add personal touch by sharing experiences from personal life like with your elderly parents, young niece, children
#Think of edge cases and error scenarios while building use-cases
Objective/Goals
It is best to get the goal clarity as soon as possible - when asking clarifying questions (Step 1), or while discussing your/company’s mission (Step 2) or when identifying users (Step 4). Before solutioning, we must check what does the business care about and specify the overall goal of the product.
In order to identify the goal, it is recommended to first prioritize (or omit) user needs / pain points based on the following parameters -
- Product lifecycle
- Users - Volume, Motivation
- Business value / Unique opportunity
- Competition
- Company mission
- Company Strengths
- Existing solutions
Pro Tip :-
#For new products, the goal could be user adoption wherein the user group and use case could be selected based on market size or gap.
#In a real world scenario, a PM will first check the data of the conversion funnel if the product is an existing one. It may be possible that the actionable issue is regarding the discovery of the product and not the usage or engagement.
For more details on how to identify product goals, read Goals & Metrics.
6) Solutions
Build a list of solutions or feature set based on key user needs, gaps and goals identified above. Take some time to brainstorm and show off your creativity. Ask the interviewer if s/he prefers a particular solution for detailing. It is recommended to have at least 3 solutions to be able to prioritize fairly. Each proposed solution must address one or more of the key user pain points and should also relate to the overall objective or goal (earlier step).
You can build a flat list of features/user stories
e.g. - Features W (registration), X (booking) , Y (forum), Z (referral) which will be prioritized later
Alternatively, you can build a list of solutions with a subset of features in each.
e.g.- App with W, X, Z features as solution 1 and Website with W, X, Y features as solution 2 (and prioritize between App and Website later)
IDEAS :-
UI-UX improvements, New APP, Feature within App or Website, AR-VR, AI-ML,
Enable Messaging, NFT, Blockchain, IOT, Robots, Drones, Autonomous vehicles,
Video conferencing, Virtual rooms, New channel/category Launches, Screen share
New Experiences - learning, live, Payments, Pricing models- Subscription, post-paid
Manual Operations, 3rd Party Vendors, Tele-calls, Video walkthroughs, Message Bots.
Pro Tip :-
#Use SCAMPER framework for creative ideas -
Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify/Magnify/Minimize, Purpose/Put to another use, Eliminate and Rearrange/Reverse
#Companies like Google love to hear moonshot ideas. Keep yourself upto date on new technologies
7) Prioritization
Evaluate and prioritise the list of solutions based on the following factors:
- Impact on the user could be assessed by determining whether the proposed solutions address a major pain point. The impact to business is analysed in terms of coherence with the mission or the selected goal.
- Cost in terms of time to implement, technology and, engineering resources required.
- Risks could be value risks, usability risks, feasibility risks or business viability risks.
PRIORITIZATION OF SOLUTIONS :-
Impact - to user & business
Cost - time, effort & feasibility
Risk - confidence
8) Recommended Solution
Now that you have put forward a constellation of propositions, it is time to finally recommend a solution and justify. Based on the prioritisation, recommend a solution with its set of features. The chosen solution should have relatively high value, low overall cost and low associated risks. You can also prioritise R&D (discovery) for longer term or moon shot solutions.
RECOMMENDATION :-
Why would people use it? Differentiator? What would you build as MVP?
How would people use it? Is it a unique opportunity or have large target audience?
Is it a Low Hanging fruit or a Quick win?
Pro Tip :-
#Select a combination of features for your MVP and describe each to build an overall picture of the recommended product
Tradeoffs/Risks
Highlight pros/cons and the risks of the recommended solution. Think of the edge-cases and negative user flows. In real world, the biggest risk for any new product is the lack of data and customer research. E.g. while building product for kids, adults should also be able to use the product in regular ways or what if some people trick the system/user flow or don’t find it interesting.
For e.g. Adding new features to an existing App can negatively impact the app size, consume more bandwidth & slows down the user in terms of experience. Churn rate, un-installs, overall session time, NPS and usage of another feature can get negatively impacted if the App feature is disliked by users.
KEY TRADEOFFS :-
Cannibalization, customer satisfaction, overuse, safety, integrity, privacy,
disparity, opportunity cost of another customer segment/ pain point/ geography
Roadmap (optional)
You can also share a contingency plan and chart a rough roadmap of the product. Based on the success of your MVP (i.e. recommended solution), you can include features from your solution list in your roadmap or add additonal ones like gamification. You can explain go to market (GTM) stratgey, share product vision and how you can iterate by having instrumentation, A/B testing, taking customer feedback and observing how users are actually using it.
9) Success Metrics
The primary expectation from the recommended solution is to achieve the goal described earlier but how would you quantify it? Measuring the product success is a vast area in itself and deserves another chapter. For the interview, it is recommended to specify 2-5 key metrics that relate best to your goals and the final product.
Product Metrics are of the following types -
- Northstar (or Goal metrics) - Be top 10 app in its category, Traffic
- Product Tracking (or Product Health metrics) - #Users, Engagement
- Guard-Rail (or Counter metrics) - Measure of tradeoffs, cannibalization
KEY METRICS :-
Adoption - Install/downloads, signups, # of users
Growth - %age Increase in New Users, DAU, MAU
Engagement metrics - DAU, MAU, session time, view, like, share, comment
Retention - Cohort activity D7, D30, DAU per MAU
Monetisation - Revenue, CTR, ARPU, Subscriptions, Revenue per Ad
Customer Satisfaction - SUS, CSAT, NPS, User ratings, Referrals
Pro Tip :-
#For new product, measure adoption as number of users using the product and active users
#For measuring engagement use #active users as the base than just #users
#Additionally, you can also track success by checking if the customers adopting the feature/product are showing the desired impact on the company goal like Users using new Insta call feature showing higher engagement on platform or not
For more details on how to identify right product metrics, read Goals & Metrics
Step 10) Summarize
Finally, outline your approach, beginning with the problem and ending with your recommendation based on the key criteria you selected.
Pro Tip :-
#Use STAR to summarize - Situation, Task, Action, Results
COMMON MISTAKES :-
Not asking enough questions to ensure common ground on product, users
Lack of mission alignment between company and product
Lack of structure in problem solving
Incomplete or no user journey
Poor customer segmentation - overly detailed, just age-based
Prioritising users, pain points, or solutions without proper reasoning
No connection between Goal-User-Painpoint-Solution
No tradeoffs or counter metrics for the recommended solution
Not clarifying #events or #unique customers in metrics
Too long a summary
Expert Tip :-
#Break the structure and pattern wherever you can. Personalize it.
Image Credits :- Cover photo: Painting ‘Departure of the Winged Ship by Vladimirkush’
If you have reached this far, you would agree that this is one of the most comprehensive guide available on 'product design' (received several thankful user notes so far).
Request you to contribute by sharing with your network (sharing options on left side) and dropping a comment (below) - especially if you think something is missing

